In recent years, the rapid adoption of cloud technology has transformed the way businesses operate, offering unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. However, alongside these benefits come new challenges, particularly in the realm of cybersecurity. As organizations migrate their data and applications to the cloud, they must also adapt their security strategies to address the unique threats and vulnerabilities present in cloud environments. One crucial component of modern cloud security is Cloud Detection and Response (CDR), a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating security incidents in the cloud.
What is Cloud Detection and Response (CDR)?
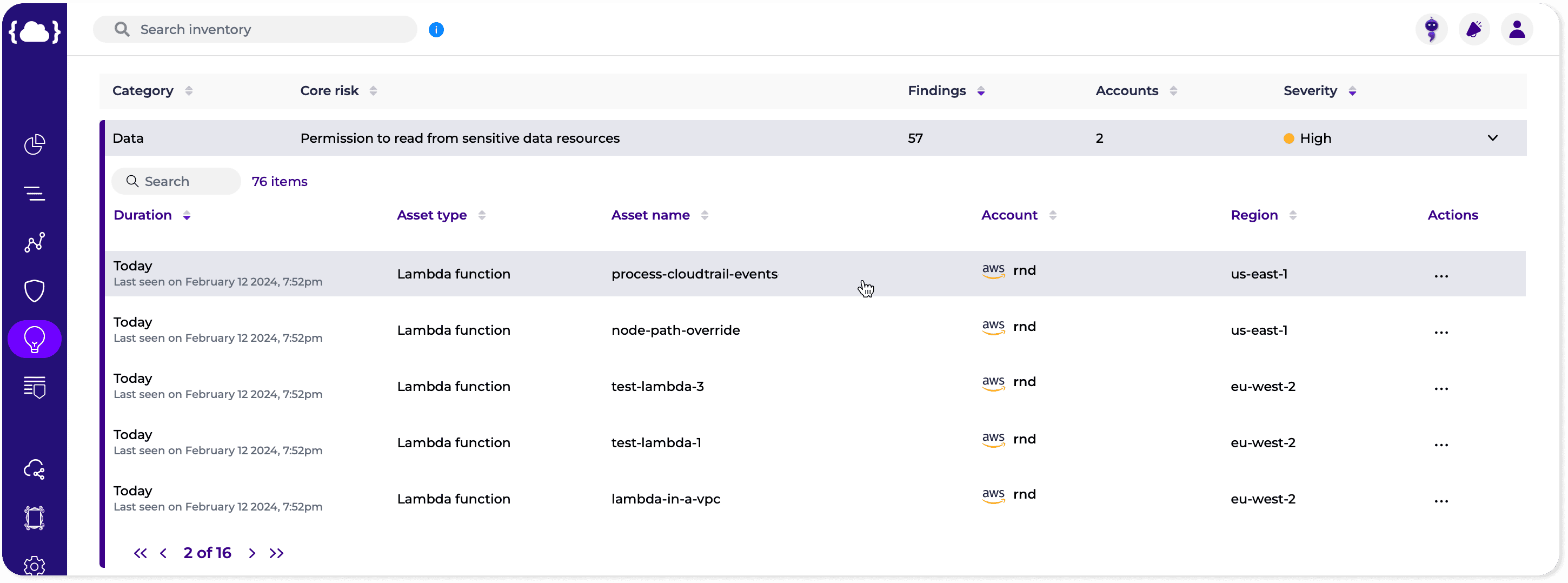
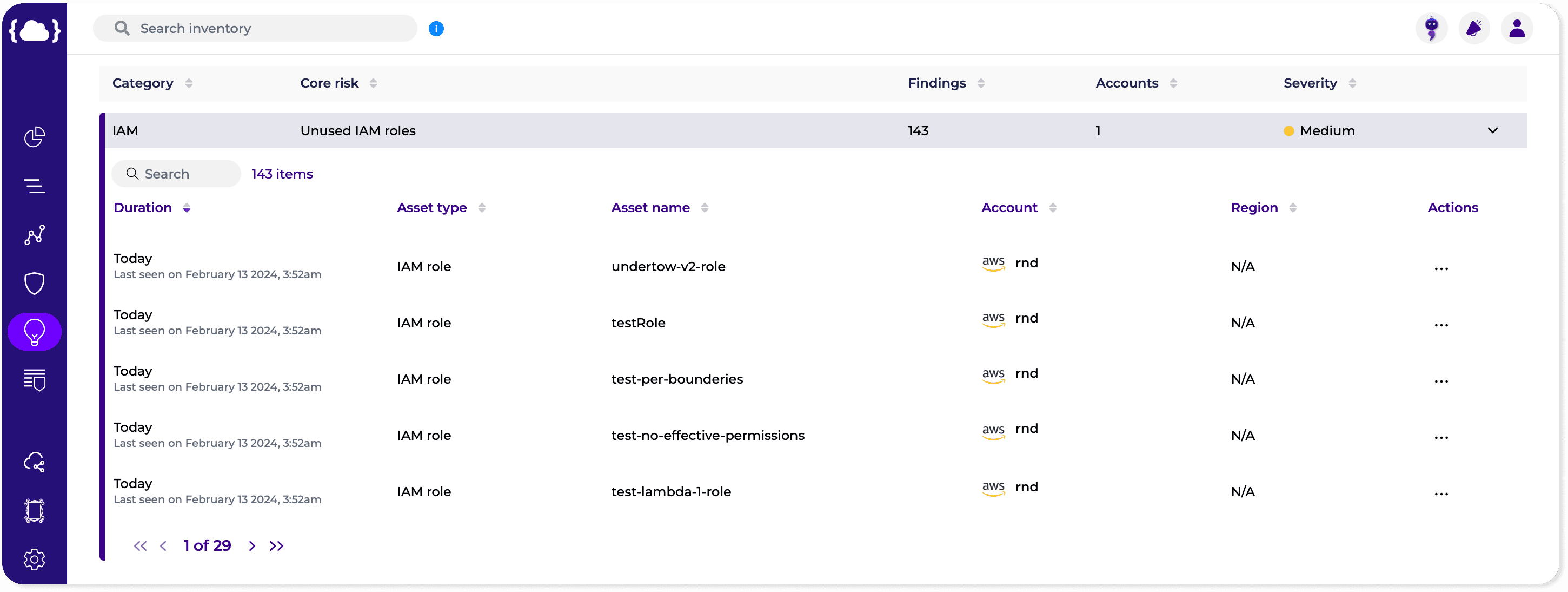
Cloud Detection and Response (CDR) is a security strategy designed to detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents in cloud environments. Unlike traditional security approaches that focus primarily on prevention, CDR takes a more holistic approach, combining advanced threat detection capabilities with rapid incident response and remediation. By continuously monitoring cloud environments for suspicious activities and anomalies, CDR solutions help organizations identify and neutralize threats before they can cause significant damage.
Why is CDR Important?
In today’s threat landscape, cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and targeted, making it essential for organizations to have robust detection and response capabilities in place. Cloud environments introduce additional complexities and challenges, such as the dynamic nature of cloud infrastructure, the proliferation of cloud-native services, and the shared responsibility model between cloud providers and customers. Without effective detection and response mechanisms, organizations risk falling victim to data breaches, malware infections, and other cyber threats that can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
How is CDR Different in the Cloud?
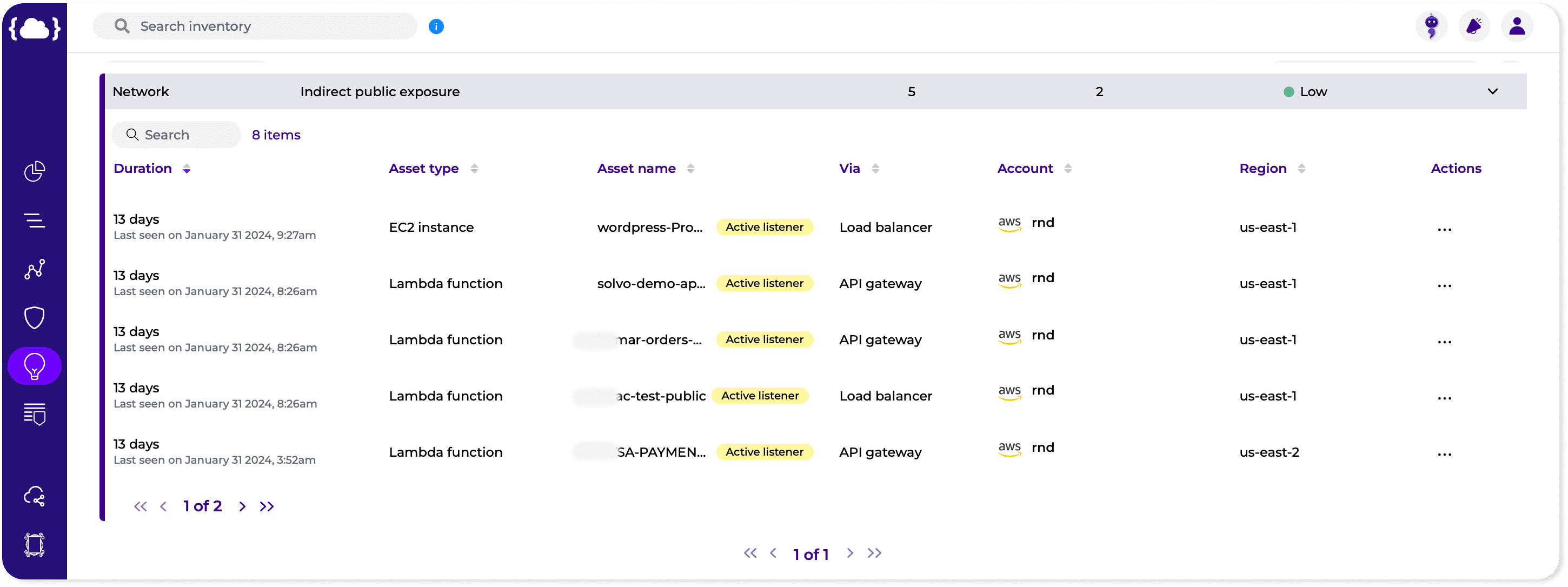
Unlike traditional on-premises environments, cloud environments operate on a distributed and dynamic infrastructure, making traditional security approaches inadequate. Cloud Detection and Response (CDR) solutions are specifically designed to address the unique characteristics of cloud environments, providing visibility and control across cloud platforms, services, and applications. CDR solutions leverage cloud-native technologies and APIs to collect telemetry data from various sources, such as virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions, enabling comprehensive threat detection and response capabilities in the cloud.
Why Response Should Include Context, Easy-to-Implement Steps, and Unique Cloud Knowledge
Effective incident response is not just about detecting and mitigating security incidents; it’s also about understanding the context surrounding the incident, providing actionable insights, and implementing remediation steps quickly and efficiently. In the context of cloud security, response actions must be tailored to the dynamic nature of cloud environments and the specific challenges they present. Here’s why the response should include context, easy-to-implement steps, and unique cloud knowledge:
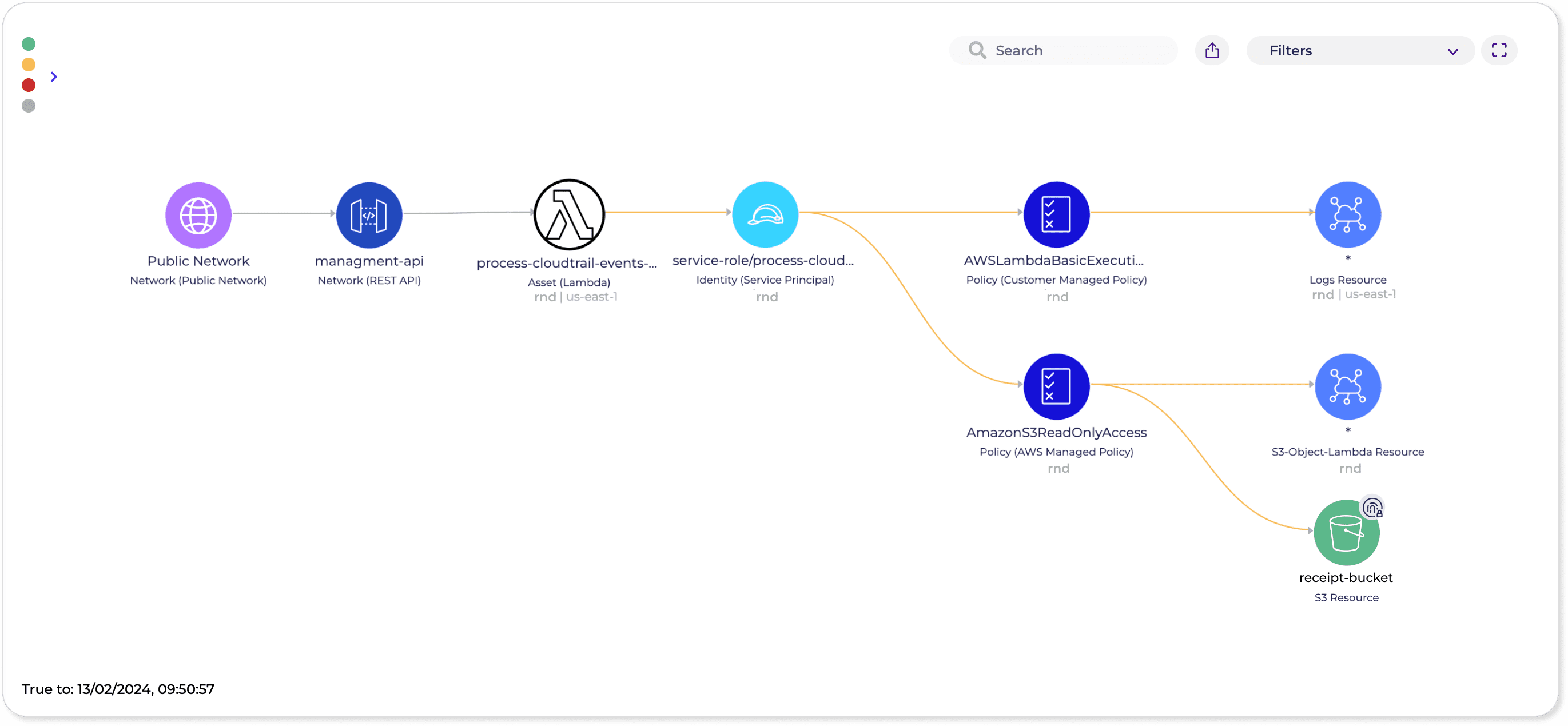
- Context: When responding to security incidents in the cloud, it’s essential to have a deep understanding of the context surrounding the incident, including the affected resources, the potential impact on business operations, and the underlying cause of the incident. By analyzing contextual information, security teams can make informed decisions about the appropriate response actions and prioritize their efforts accordingly.
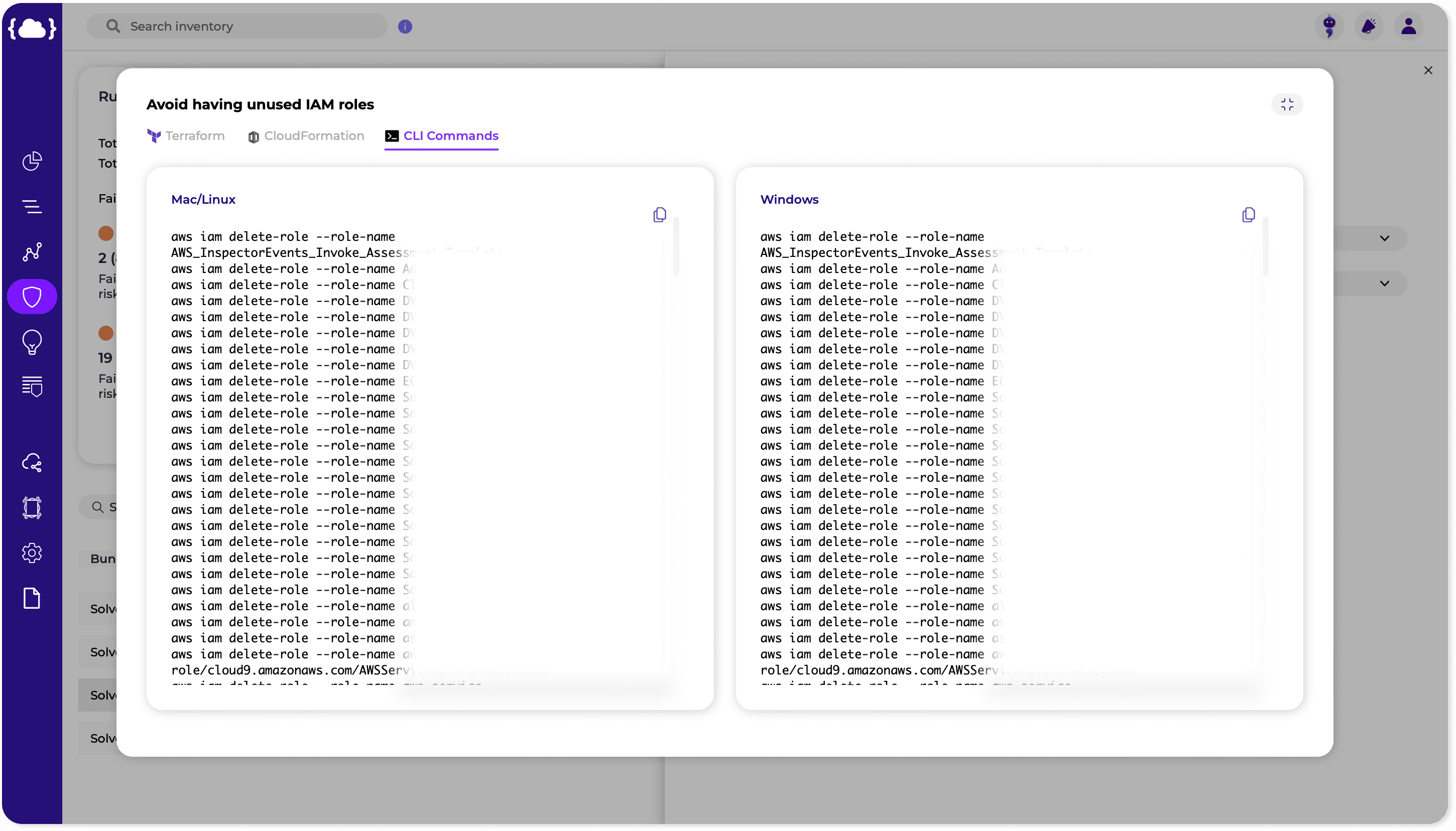
- Easy-to-implement Steps: In the fast-paced world of cloud security, time is of the essence. Response actions must be easy to implement and execute quickly to minimize the impact of security incidents. By providing pre-defined response playbooks and automated remediation workflows, CDR solutions enable security teams to respond to incidents rapidly and effectively, reducing the time to detect and mitigate threats.
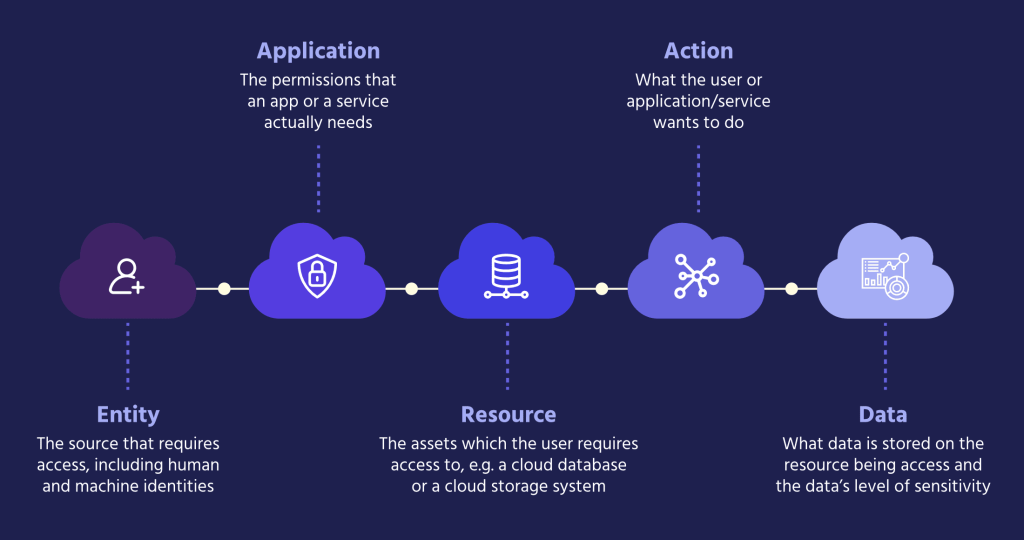
- Unique Cloud Knowledge: Cloud environments have their own set of nuances and intricacies that require specialized knowledge and expertise to navigate effectively. Response actions in the cloud must take into account the unique characteristics of cloud infrastructure, such as ephemeral resources, auto-scaling capabilities, and shared responsibility models. By leveraging cloud-native technologies and best practices, security teams can tailor their response strategies to the specific requirements of cloud environments, ensuring comprehensive protection against emerging threats. When considering a new CDR solution, you should consider the product’s ability to process context in multiple dimensions, bringing together IAM, network, data, vulnerabilities, secrets, and more. A multi-dimensional approach will reduce false positives, give a better context, and prioritize what matters most. The response should also be customized and built uniquely for the detected issue so that the SOC and DevOps teams can work together productively.
To learn how Solvo helps its customers detect and remediate issues effectively, book a demo!