In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, ensuring robust security measures is paramount. As organizations increasingly migrate their workloads to the cloud, the need for comprehensive security solutionsbecomes more critical.
Cloud security is a complex undertaking though. Cloud environments are fluid and geographically dispersed, with resources dynamically provisioned and scaled across multiple locations. This makes it di cult to establish clear perimeters and implement consistent security controls, as traditional on-premises security approaches often fall short.
With numerous services, APIs, and endpoints exposed, cloud environments present a larger attack surface for malicious actors.
Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in any layer of the cloud stack, including misconfigurations, software bugs, or insecure access controls, making it crucial to maintain comprehensive security across all levels. Moreover, the use of unauthorized cloud services or applications (shadow IT) can create significant security risks and blind spots.
Navigating the regulatory landscape and implementing controls to meet various compliance mandates adds another layer of complexity to cloud security.
On top of that, the need to keep pace with the rapid evolution of cloud technologies and constantly emerging threats is placing a huge burden on organizations, many of which lack the in-house talent or resources to handle these challenges.
The multi-faceted nature of cloud security threats requires organizations to integrate various security tools and platforms from different vendors into a cohesive security ecosystem that can protect data, applications, and resources. The challenge of dealing with multiple solutions has led to the emergence of converged cloud security offerings, most notably cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP).
CNAPP combines a comprehensive suite of capabilities to secure the entire cloud-native application lifecycle, from development and deployment to runtime and threat detection. It prioritizes protecting both the application itself and the cloud infrastructure it runs on, providing a unified view of security across the entire stack.
CNAPP typically includes functionalities of both CIEM and CSPM but goes beyond them by adding application security tools like container security, API security, runtime threat protection, and more. As such, CNAPP is typically more suitable for organizations with diverse cloud security needs. However, a full-fledged CNAPP solution might be overkill for many organizations that don’t build their own software or ones that prioritize secure cloud access over other concerns.
For example, organizations that handle large amounts of highly sensitive data stored in the cloud may prioritize the prevention of unauthorized access to resources hosting such data over other security concerns. For these customers, leveraging the potential synergies between CIEM and CSPM allows for the implementation of an effective access-first approach to cloud security.
Before delving into their convergence, let’s briefly outline the individual roles of CIEM and CSPM.
CIEM focuses on governing and managing permissions and entitlements within the cloud infrastructure. It ensures that users have the appropriate access levels, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
CSPM, on the other hand, is designed to monitor and enforce security configurations in cloud environments. It evaluates the cloud environment against established security best practices, identifying and remediating improper system and infrastructure configurations. These misconfigurations create vulnerabilities by allowing unauthorized access to systems and data, and cause other security issues.
In a recent report on Solvo’s adaptive cloud security approach, 451 Research, part of S&P Global Market Intelligence, has noted that “some of the most pressing security pain points include managing configurations, identities and permissions in cloud resources. In recent years, the CSPM and CIEM segments have emerged to address these challenges.”
The integration of CIEM and CSPM capabilities provides organizations with comprehensive visibility and understanding of access-related risks across their cloud infrastructure, facilitating the management of identities, entitlements and system configurations. It enables security teams to find out which users have access to specific resources, what permissions they have, how they are using it, which resources are at risk of unauthorized access, and much more.
The convergence of CIEM and CSPM becomes even more potent when contextual analysis is applied. Contextual analysis involves understanding the nuanced relationships between different elements within the cloud infrastructure.
Unlike traditional identity and access management approaches where permissions are typically assigned based on user roles and responsibilities, dynamic cloud environments require constant evaluation and updated security policies and controls. In such a chaotic environment where numerous components are always in motion, access permissions and entitlements should be determined by a more comprehensive, real-time understanding of user (human and machine) activities, rather than relying solely on static roles.
An effective contextual analysis along these lines should be based on integrating insights across several fields:
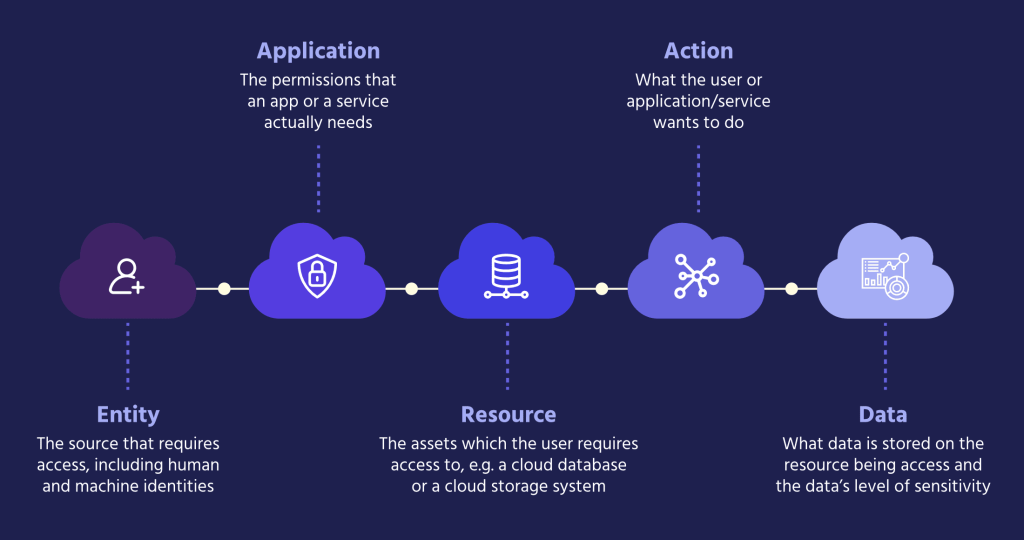
By integrating CIEM and CSPM through contextual analysis, and constantly analyzing configurations, relationships, and activities across these dimensions, organizations gain more in-depth and holistic insight into their cloud security posture. This enables security teams to address both identity-related risks and configuration vulnerabilities, maintain consistent security practices across the entire cloud environment, and make informed decisions at speed.
Moreover, adding a context layer on top of a combined CIEM-CSPM solution empowers security teams to achieve important benefits that are difficult to attain otherwise:

A converged CIEM-CSPM approach enhanced with contextual information security empowers security teams to assess risks with greater accuracy, prioritize remediation based on asset criticality (e.g. resources hosting sensitive data), blast radius, vulnerability severity, and other factors, and implement access policies and entitlements that align with the actual level of threat.
Contextual analysis facilitates the implementation of adaptive access controls. Instead of relying on static access permissions, organizations can dynamically adjust access levels based on the context, granting elevated privileges only when necessary and revoking them when not in use.
The contextual approach enables security teams to automate the processes of applying and enforcing access policies, which are currently labor-intensive and error-prone while reducing operational burden.
By identifying and rectifying access-related security issues in real-time based on context, the combined CIEM and CSPM approach reduces the window of vulnerability, and enhances the overall resilience of cloud environments.
Providing a detailed understanding of the context surrounding activities made by user and service accounts, and resource configurations, contextual analysis helps in identifying and mitigating potential regulatory risks. This is crucial for industries with stringent compliance requirements.
As cloud security continues to be a top priority, the integration of CIEM and CSPM emerges as a practical and effective solution for safeguarding digital assets in the cloud. While cloud security threats continue to grow in frequency, scale and complexity, mitigating identity-related threats and resource misconfigurations remains a top concern for many organizations that take an “access-first” approach to cloud security.
The convergence of CIEM and CSPM, fueled by contextual analysis, represents a formidable strategy to achieve a level of cloud security that surpasses the sum of its parts. By correlating infrastructure relationships, entitlements, and misconfigurations, organizations can dynamically assess risks, automatically adapt access policies and controls based on contextual insights, and fortify their cloud environments against an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Solvo’s adaptive cloud security offering was designed around these principles. Leveraging advanced machine learning and context-aware analysis, Solvo combines CIEM and CSPM capabilities under a unified, multidimensional access-focused CNAPP solution.
Solvo’s platform continuously assesses human and machine identities, cloud resources, access permissions and entitlements, and automatically detects and remediates vulnerabilities and misconfigurations based on real-time risk analysis, ensuring least-privilege access and a robust cloud security posture.
The recently published 451 Research report, “Solvo tackles CNAPP with adaptive cloud security and deep application analysis,” highlighted Solvo’s ability to “create policies automatically, as well as a combination of CIEM and CSPM, data security posture features, and patented application analysis. Adaptive remediation is a key differentiator.”
